Healthy Gut & Inflammation
Until recently, the gastrointestinal tract was largely ignored by Western medicine. It was thought it was simply the place where nutrients were digested. However, recent research has shown that maintaining a healthy gut is essential to overall health. In fact, the intestinal tract plays a key role in so many biological processes it is hard to list them all. Here are but a few examples:
- Digestion of food into small particles.
- Absorption of critical nutrients like amino acids, carbohydrates, fats, and minerals.
- Elimination of waste products such as heavy metals via bile.
- Immune function—the intestinal tract is the LARGEST immune organ.
- Barrier function—keeping out bacteria, viruses, and fungi as well as other toxic substances from being absorbed. This is compromised in conditions such as IBD, IBS and “leaky gut.”
- Inflammation—due to its intimate relationship in immune function and its regulation of foreign substances from crossing into our blood stream, the gut plays perhaps The key role in inflammation.
Put simply, if your gut is out of balance, you cannot achieve optimal health.
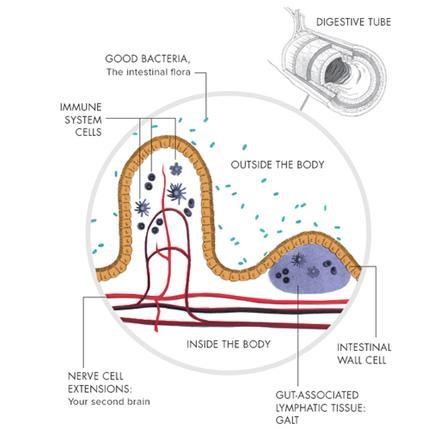
The first layer of cells in the GI tract forms the “mucosa.” These cells sit very close one another forming “tight junctions” (see diagram below) to prevent foreign organisms or substances from entering our bodies. They also secrete a protective mucous layer and IgA’s which are protective antibodies for the same purpose.
Deeper within the wall of the intestines the immune system is housed in the form of lymph nodes in what is called the Gut Associated Lymphatic Tissue (GALT). The deeper levels of the intestinal walls also contain the Enteric Nervous System (ENS) which is a nervous system dedicated to the gut itself and is only partially controlled by Central Nervous System (CNS).
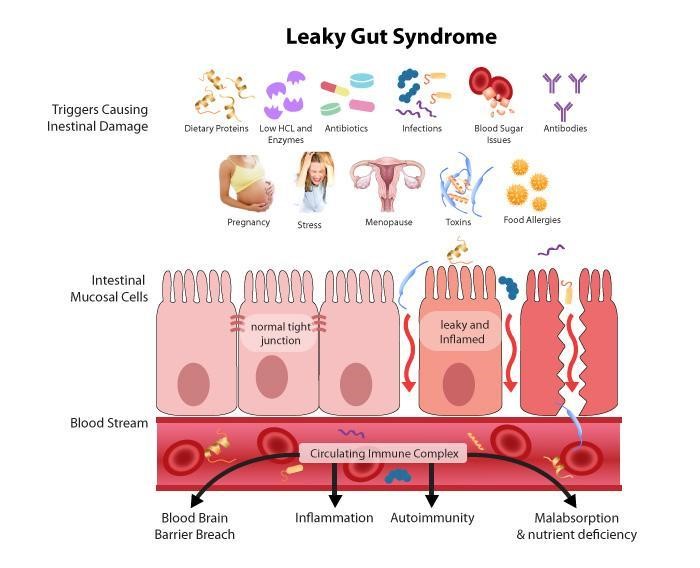
Many factors can affect the integrity of this intestinal barrier, wear down the mucous protection, decrease IgA production and finally break down the “tight junctions” between the cells of the intestinal tract making them permeable to substances. When this happens even whole bacteria and viruses can “leak” through the gut lining into your blood stream which is not desirable. This phenomenon is called “increased intestinal permeability,” and it is commonly referred to as “leaky gut”.
When you have a leaky gut, your immune system is exposed to foreign materials, toxins and organisms which triggers the immune system to attack using powerful inflammatory compounds. This can set off a tragic downward spiral where the gut becomes more permeable, systemic inflammation takes off like a fire in a forest, and your “leaky gut” gets worse. Systemic inflammation, not only further damages the intestinal wall, and worsen absorption, but also it paves the ground for chronic diseases, such as DM2, autoimmune diseases, such as Rheumatoid arthritis, and Multiple Sclerosis.
As you can see in the pictures below, some of the factors that lead to increased intestinal permeability are:
- Stress—physical and psychological
- Alcohol
- Medications—anti-inflammatories (NSAIDs like ibuprofen), antibiotics
- Toxins
- Small Intestine Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO)
- Chronic illnesses: Diabetes, Autoimmune illnesses
- Food allergies
- Trauma
Modern life style compromises our intestinal tracts through factors such as stress, anti-inflammatory medicine (NSAIDs like ibuprofen), antibiotics, poor diets, alcohol consumption and smoking to name a few.
How can we heal our gut, and restore its optimal functions?
Zinc and L-glutamine both reduce intestinal permeability (“leaky gut”) closing the tight-junctions between intestinal cells and thus protecting us from over-activating our immune systems and setting off inflammation. Furthermore, L-glutamine is the preferred fuel for intestinal and immune cells over glucose. L-Arginine raises the levels of IGF-1 (the active form of Growth Hormone), a critical component in maintaining “Occludin” integrity, a protein which “seals” the space between intestinal cells preventing “leaky gut”. L-arginine, is also a precursor to Nitric Oxide (NO), which is an essential transmitter for the proper function of the GIT.
Antioxidants like vitamin C and glutathione, also play a role, since they are important protectors of the mucous layer and cells of the intestinal tract, shielding against the damage done from intestinal inflammation.
Recent Posts
-

Types of STD Tests: Blood, Urine, Swab and Rapid Tests Explained
STD testing is considered essential for early detection, accurate diagnosis, and effective treatment of sexually transmitted infections. Many STDs show little or no symptoms, making regular screening an important part of sexual health and wellbeing. January 16, 2026 -

How Modern Labs Detect STDs: The Science Behind the Tests
Sexually transmitted infections can often stay silently in the body, sometimes creating subtle changes that leave a person uncertain about what is happening. Modern diagnostics and STD/ STI lab tests help bring clarity by studying tiny pathogens that the body is being exposed to long before it becomes an actual health risk.
January 06, 2026 -

Multivitamin IV Drip: How Beneficial Are They?
A Multivitamin IV Drip is a sterile infusion that combines nutrients such as vitamin C, B-complex vitamins, magnesium, and calcium in a balanced, hydrating solution. At Health Call, this popular treatment is used to support overall hydration ...
December 10, 2025 -

Understanding the STD Test Window Period
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) remain a significant public health concern worldwide, and early detection is key to both treatment and prevention of transmission. One of the most crucial, yet often misunderstood, aspects of STD testing is the window period.
August 07, 2025 -

HIV and AIDS Symptoms in Women
HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) and AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome) affect millions worldwide, but the symptoms in women can often be misunderstood, overlooked, or mistaken for other conditions.
August 07, 2025